
Format Ext2 In Windows Free Utility Designed
GParted is a Linux program you can download it and install it on your favorite Linux distribution. GParted is a free utility designed to partition and format drives in a wide variety of filesystems, some of which include, ext2, ext3, ext4, NTFS, fat32, fat16, etc. In this section we are going to be using GParted.
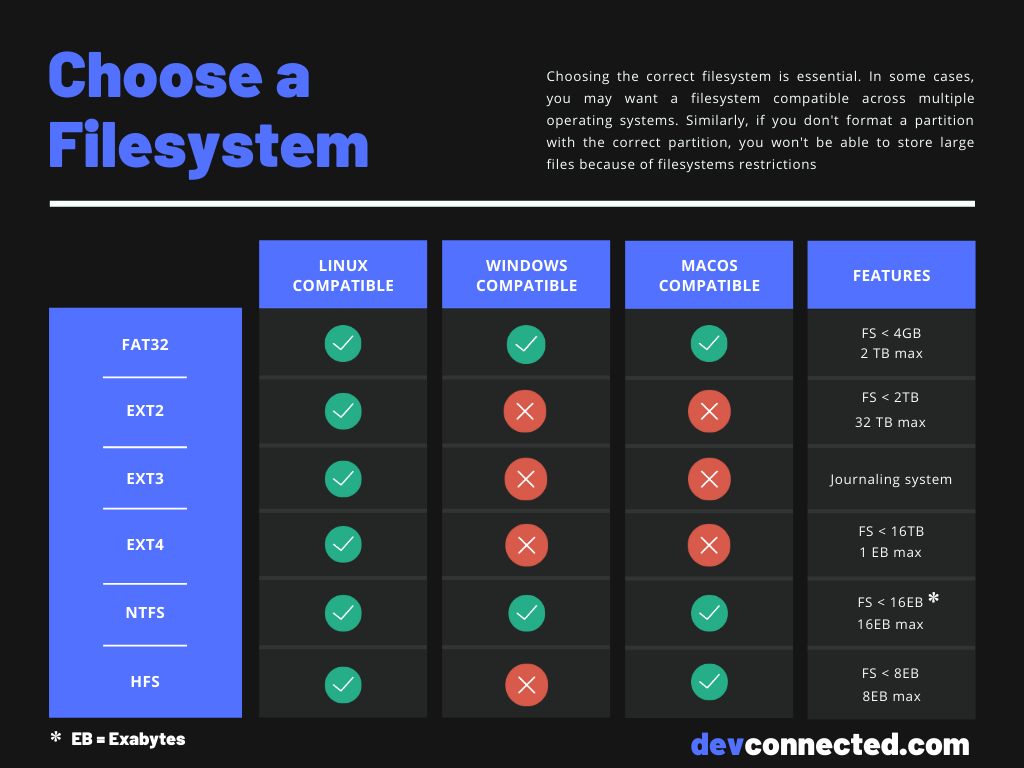
I even tried GParted, which totally failed creating any new partitions on the drive. Ubuntu would let me format the drive but then “ lshw” would not detect nor list it. Sometimes the LiveCD would detect the drive and sometimes it would not. The LiveCD would recognize the hard drive half of the time. However, for some reason I just could not get it to work reliably with any Linux LiveCD. One drawback of choosing Linux filesystems is that they are not readable by Windows not that it really matters that much, since you will still be able to clone any filesystem, but sometimes you want to use the hard drive to store other files beside your Clonezilla images.5) Click on “Add” button to save changes.6) Finally, on the main screen, click on the green checkmark to apply changes and start the process.The process will take a few minutes, depending on the size of the hard drive.I recently bought a 2TB external hard drive I was planning to use with Clonezilla Live.
Issue the following command at your shell prompt (Again, remember that you will lose all the data in the drive after this, so make sure you have any files you wish to save backed up): sudo fdisk /dev/sdbAt the “ Command (m for help)” prompt, delete the current partition by typing “ d“, then, save changes by typing “ w“.To create new partition, issue again the following command at the shell prompt: sudo fdisk /dev/sdbAt the “ Command (m for help)” prompt, type “ n” to create a new partition, then type “ p” to make it a primary partition. Make sure you identify it correctly because after this you will lose all the data in your drive. For this example lets say we identified it as /dev/sdb1 this means that your drive will be /dev/sdb.We have identified our drive for this example as being /dev/sdb, yours could be /dev/sdd, /dev/sde, etc. If you are in a similar situation here’s what you need to do:To identify your hard drive, issue the following command in your shell prompt: sudo fdisk -lLook for the device file name identifying your drive’s partition.
The following table lists some of the most common ones: 82 Linux swap / SoOnce done choosing the partition type, enter “ w” to save changes and you are done creating your partition table, now you need to format it.In our example, we created a partition table for Linux now we are going to format this partition as Ext3. You can get a complete list of identifiers by typing “ L” at the “ Command (m for help)” prompt. Then type “ t” to specify partition type here you are going to be asked a hexadecimal number that indicates whether the partition is fat32, ext3, ext4, etc, for example if we want an ext3 partition we would enter “ 83“.
Run the following command to eliminate the reserved space: sudo tune2fs -m 0 /dev/sdb1This will set the reserved space from taking-up 5% of the drive to 0%. This is totally unnecessary for a USB external hard drive if you are only going be using it to store data and not to run an operating system.To get rid of this reserved space, identify your partition using the command sudo fdisk -lFor our example we are going to assume we identified the partition in our drive as /dev/sdb1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
